
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 CAS Key Laboratory of Quantum Information, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei 230026, China
2 CAS Center for Excellence in Quantum Information and Quantum Physics, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei 230026, China
3 Hefei National Laboratory, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei 230088, China
Modulation of a vector light field has played an important role in the research of nanophotonics. However, it is still a great challenge to accurately measure the three-dimensional vector distribution at nanoscale. Here, based on the interaction between the light field and atomic-sized nitrogen-vacancy (NV) color center in diamonds, we demonstrate an efficient method for vectorial mapping of the light-field distribution at nanoscale. Single NV centers with different but well-defined symmetry axes are selected and then interact with the same tightly focused light field. The excitation of a single NV center is related to the angle between the NV center axis and the polarization of the light field. Then the fluorescence patterns of different NV centers provide the information on the vectorial light field distribution. Subsequently analyzing the fluorescence patterns with the help of a deep neural network, the intensity and phase of the light-field vectorial components are fully reconstructed with nanometer resolution. The experimental results are in agreement with theoretical calculations. It demonstrates that our method can help to study light–matter interaction at nanoscale and extend the application of vector light fields in research on nanophotonics.
light-field measurement nitrogen-vacancy center tightly focused light field Chinese Optics Letters
2023, 21(7): 071202
中国科学技术大学中国科学院量子信息重点实验室,安徽 合肥 230026
金刚石中的氮-空位(NV)色心在室温下具有稳定的荧光发射,超长的电子自旋相干时间以及许多优良的光学性质,可以对电磁场,温度进行高灵敏度表征。光纤传感技术近几年来发展迅速,在电力、化工、交通、医疗、环保及**等领域得到广泛应用。光纤体系由于其集成度、实用性高以及操作便捷性,且具有优良的传输光能力,损耗较低,可与NV色心结合,形成一种高集成化、高灵敏度的便捷性传感系统,未来将会作为传感器件投入到许多领域的应用中,例如对生物细胞、材料温度、磁场等物理量的高灵敏度测量。本综述主要介绍NV色心体系的光纤量子传感技术的工作原理、实现方式以及在相关领域的应用。
氮-空位色心 光纤 量子传感 激光与光电子学进展
2023, 60(11): 1106001

Haobin Lin 1,2,3Ce Feng 1,2,3Yang Dong 1,2,3Wang Jiang 1,2,3[ ... ]Fangwen Sun 1,2,3
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 CAS Key Laboratory of Quantum Information, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei 230026, China
2 CAS Center for Excellence in Quantum Information and Quantum Physics, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei 230026, China
3 Hefei National Laboratory, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei 230088, China
4 National Key Laboratory of ASIC, Hebei Semiconductor Research Institute, Shijiazhuang 050051, China
Nitrogen-vacancy color centers can perform highly sensitive and spatially resolved quantum measurements of physical quantities such as magnetic field, temperature, and pressure. Meanwhile, sensing so many variables at the same time often introduces additional noise, causing a reduced accuracy. Here, a dual-microwave time-division multiplexing protocol is used in conjunction with a lock-in amplifier in order to decouple temperature from the magnetic field and vice versa. In this protocol, dual-frequency driving and frequency modulation are used to measure the magnetic and temperature field simultaneously in real time. The sensitivity of our system is about and , respectively. Our detection protocol not only enables multifunctional quantum sensing, but also extends more practical applications.
quantum sensing temperature measurement magnetic field measurement Chinese Optics Letters
2023, 21(1): 011201

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 CAS Key Laboratory of Quantum Information, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei 230026, China
2 CAS Center for Excellence in Quantum Information and Quantum Physics, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei 230026, China
3 Hefei National Laboratory for Physical Science at Microscale, Department of Physics, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei 230026, China
The nitrogen vacancy (NV) center in diamond has been well applied in quantum sensing of electromagnetic field and temperature, where the sensitivity can be enhanced by the number of NV centers. Here, we used electron beam irradiation to increase the generation rate of NV centers by nearly 22 times. We systematically studied the optical and electronic properties of the NV center as a function of an electron irradiation dose, where the detection sensitivity of magnetic fields was improved. With such samples with dense NV centers, a sub-pico-Tesla sensitivity in magnetic fields detection can be achieved with optimal controls and detections.
quantum sensing nitrogen vacancy center generation electron irradiation Chinese Optics Letters
2020, 18(8): 080201

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 CAS Key Laboratory of Quantum Information, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei 230026, China
2 CAS Center for Excellence in Quantum Information and Quantum Physics, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei 230026, China
Forward-scattering-light interferometry has become the most commonly used position detection scheme in optical levitation systems. Usually, three-set detectors are required to obtain the three-dimensional motion information. Here, we simplify the three-set detectors to one set by inserting a Dove prism. We investigate the role of a Dove prism in the position measurement process with an optical levitation system in vacuum. The relationship between the power spectral density and the rotation angle of a Dove prism is experimentally demonstrated and analyzed. This work shows that the Dove prism can greatly reduce the complexity of the experimental setup, which can be applied to compact optical levitation systems for studies in metrology, quantum physics, and biology.
090.1970 Diffractive optics 140.7010 Laser trapping Chinese Optics Letters
2019, 17(6): 060901
中国科学技术大学量子信息重点实验室, 安徽 合肥 230026
光学显微镜的出现为细胞等微观结构的研究打开了新的大门,然而衍射极限的限制使得更加精细的结构难以探测。近年来,一些充满创造性的方法突破了衍射极限,达到纳米级分辨率。氮-空位(NV)色心是金刚石中一种常见的发光缺陷,由于其具有明亮而稳定的发光性质和较长的电子自旋相干时间而被广泛应用于量子计算与量子测量中;同时,NV色心在超分辨成像技术中也发挥着巨大作用,通过与各种超分辨成像显微镜的结合,实现了对NV色心的纳米级分辨率成像,而且进一步实现高空间分辨率的量子传感。本文简单介绍了NV色心的结构与性质,以及各类成像技术的基本原理;对NV色心与超分辨成像结合的各项技术实验成果进行了归纳与比较,并对其应用进行了总结与展望。
成像系统 超分辨成像 衍射极限 NV色心 荧光显微镜 激光与光电子学进展
2017, 54(3): 030003
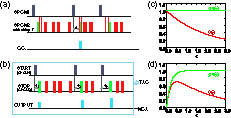
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of Quantum Information, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei 230026, China
2 Synergetic Innovation Center of Quantum Information and Quantum Physics, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei 230026, China
The measurement of the second-order degree of coherence [g(2)(τ)] is one of the important methods used to study the dynamical evolution of photon-matter interaction systems. Here, we use a nitrogen-vacancy center in a diamond to compare the measurement of g(2)(τ) with two methods. One is the prototype measurement process with a tunable delay. The other is a start-stop process based on the time-to-amplitude conversion (TAC) and multichannel analyzer (MCA) system, which is usually applied to achieve efficient measurements. The divergence in the measurement results is observed when the delay time is comparable with the mean interval time between two neighboring detected photons. Moreover, a correction function is presented to correct the results from the TAC-MCA system to the genuine g(2)(τ). Such a correction method will provide a way to study the dynamics in photonic systems for quantum information techniques.
160.2220 Defect-center materials 270.5290 Photon statistics Chinese Optics Letters
2016, 14(7): 072701
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of Quantum Information, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei 230026, China
2 National Synchrotron Radiation Laboratory, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei 230029, China
By using CdSe/ZnS quantum dots (QDs), we study the effect of cavity quantum electrodynamics on the coupling of the microtoroid cavity. When with whispering gallery (WG) modes, the microtoroid cavity demonstrates high quality factor and small mode volume at visible wavelengths. Accordingly, fiber tapers allow QDs to adhere into the cavity and further permit the control of site-selected coupling. From the luminescence spectra, QDs are modulated effectively by cavity modes. Variable modulations are observed by changing QD coupling conditions. Therefore, based on experimental and theoretical research, strong and tunable Purcell enhancement can be realized by this system.The authors thank Jinming Cui and Chunhua Dong for their helpful discussion. This work was supported by the National Fundamental Research Program of China (No. 2006CB921900), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 60537020 and 60621064), and the Knowledge Innovation Project of the Chinese Academy of Sciences.
光纤锥 微芯圆环 腔量子电动力学 量子点 020.5580 Quantum electrodynamics 140.3945 Microcavities 060.2310 Fiber optics Chinese Optics Letters
2010, 8(7): 709





